Mughal architecture reached its zenith during his reign and the practice of using marble throughout the building and decorating the walls with semi-precious stones in the form of flowers became famous.
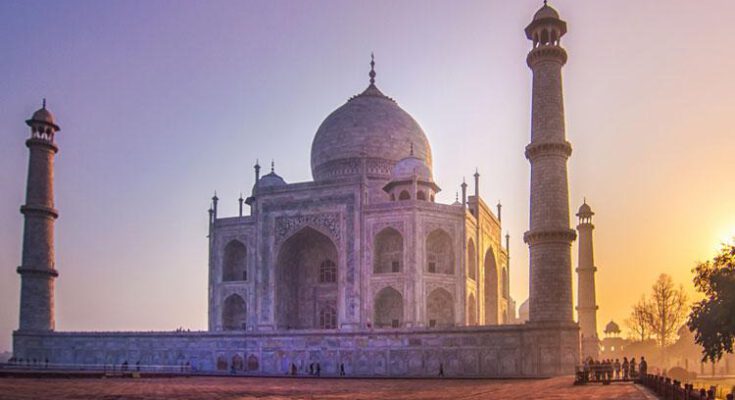
This method of decoration, called petradura, became more popular under Shah Jahan, who used it extensively during the construction of the Taj Mahal, which was considered a jewel of architectural art.
After Akbar, his son Jahangir also built many buildings. He also wrote a book named Tuzuk-e-Jahangiri. Very few buildings were built during Jahangir’s reign, in keeping with his father’s architectural work, but two buildings of his time are of particular interest.
One is the tomb of Akbar, whose special features have been discussed earlier. The second is the tomb of Itimad-ud-daulah in Agra, which was built by his daughter and Jahangir’s wife Nur Jahan. This tomb was completely made of white marble and was decorated with low value stones embedded in marble.
Jahangir’s son Shah Jahan was a great builder of palaces and floors. He built the magnificent mausoleum Taj Mahal over the tomb of his beloved wife Mumtaz Mahal, which at that time cost 50 lakh rupees to build. Even today the Taj Mahal is considered one of the seven wonders. Taj Mahal is world famous for its beauty and uniqueness.
Humayun’s tomb had a colossal marble dome which was built in Delhi at the beginning of Akbar’s reign and may be regarded as the ancestor of the Taj Mahal. The double dome was and is another feature of this building. Jahangir’s mausoleum, which was built by Shah Jahan in the beginning at a place called Shahdara in Lahore, though not as famous as the Taj, is a fine piece of art.
He was a greedy ruler and had taken his father Shah Jahan as a prisoner. He did not build any buildings. Whatever the buildings of his reign, the most important of which was the Lahore Mosque, which was built in 1674 AD. were only weak imitations of the old ideals.
Through this article, we are telling you about the Mughal architecture, which is still the center of tourist attraction.
Akbar, the son of Humayun, the greatest and influential ruler of the Mughal period, built many places that are increasing India’s pride today. Akbar’s activity was not limited only to the masterpieces of architecture, but he also built some forts, rural houses, towers, inns, schools, ponds and wells. Akbar built a large number of schools and colleges for higher education in Agra and Fatehpur Sikri. He wanted everyone in his empire to be able to get an education.
Akbar was the first Mughal ruler during whose reign construction work was done on a large scale. The range of his construction includes the most famous fort of Agra and the huge Red Fort which has many grand gates. Due to his tolerance towards Hindus, sympathy with their culture and his policy of favoring them, he used Hindu styles of architecture in many of his buildings. The decorative features of these buildings are imitations of the decorative features found in Hindu and Jain temples.
Akbar’s Tomb
Tomb of Akbar the Great. This mausoleum located in Sikandra is spread over 119 acres. Sikandra is situated 13 km from Agra Fort, 8 km west-north-west of the city center on the Mathura Road. The mausoleum building is a small pyramid shaped five storied monument made of dark red sandstone and enriched with features in white marble.
Akbar himself selected the site for his tomb and started the construction of Sikandra. Its construction was later completed by his son Jahangir. About 1 km away from the mausoleum is the mausoleum of Mariam-uz-Zamani, wife of Emperor Akbar and mother of Jahangir.
Akbar’s tomb is constructed of marble and red sandstone and exhibits a unique blend of Muslim and Hindu architectural styles. The marble used in it is beautifully carved and decorated with ornaments. The tomb is built on an area of 105 square meters and compass was used for precision in construction.
It is situated in the middle of a beautiful garden surrounded by high walls. The specialty of this mausoleum is its door, which is called Buland Darwaza. Starting from the door, a wide path leads to the tomb. This door is built on an arch and has four minarets made of marble.
If seen, more than the tomb, its door attracts people towards itself. The rest of the tomb is constructed of red sandstone, using Mughal architecture. Akbar’s tomb is a five-storied building and is pyramidal in shape.
The tomb built on the top floor of the mausoleum is not genuine as the original tomb was built below ground level. A monastery has been built around the lowest floor which is divided into several parts with huge arches and pillars.
The four storeys of the mausoleum have verandahs with groups of arches and archways on each side. Some of the second floor has pyramid shaped ceilings which are constructed by marble while the rest are dome shaped. There is a small square room in each corner of the third floor.
The top floor of this building is constructed by white marble. The assembly hall located in the tomb is of square shape, and is open towards the sky. The tomb has a central courtyard surrounded by slender arches on all sides.
This courtyard is divided into sections with patterned roofs. In the center of the mausoleum complex is a square platform on top of which a false tomb has been built, which has been constructed of white marble.
The excavation work of Arabesque and flower patterns has been done on this tomb. The center of all the buildings is made high like a tomb, which has beautiful panels which are decorated with mosaic work. Which is very attractive to watch. Many tourists come to see Akbar’s fort and are amazed to see its architecture.
Fatehpur Sikri

Fatehpur Sikri is a city in Agra district of Uttar Pradesh state. The Mughal Emperor Akbar founded the city in 1569 and served as the capital of the Mughal Empire from 1571 to 1585. Akbar named the city as Fatehabad, Fateh in Arabic as victorious.
The city serves as a treasure trove of beautiful Indian Mughal architectural monuments. Today it has become a historical city situated at a distance of about 40 km from Agra.
It was from here in 1573 that Akbar marched to conquer Gujarat. While returning after conquering Gujarat, he named Sikri as ‘Fatehpur’ (Victory City). Since then this place is called Fatehpur Sikri. Fatehpur Sikri can be called a fortified city.
Buland Darwaza, Badshahi Darwaza, Panch Mahal, Jodhabai Mahal and Birbal Bhawan are some of the landmarks of Sikri. Diwan-e-Khas, Diwan-e-Aam, Anoop Talab and Daulat Khana are also made on sight. The whole fort is made of red stones. There is a special Anoop Talab here. It is a small pool, which is connected by small bridges. It was here that Tansen mesmerized the court with his music.
There is another small building in this fort, the name is Aankh Micholi. It is said that this was Akbar’s favorite place. It was here that he used to play games with his wives and entered the fort only through a 175 feet high lofty door. It is said that the Buland Darwaza is the highest gate in Asia.
The buildings here can be seen in two ways, either you move from bottom to top or come down from top by entering through the elevated door. To reach the Buland Darwaza one has to come up 13 meters of stone stairs. Even after almost five hundred years, it looks fresh and new.
The nets here are very beautiful. There is a Badshah Darwaza in this courtyard, through which Emperor Akbar used to enter the mosque and the dargah. It is right in front of the mosque.
On reaching near the Badshahi Darwaza, one can see the stairs going down, which lead to the royal residential area, where all the residential buildings, entertainment facilities were built. Fatehpur Sikri also has a religious significance today. Tourists come here from far and wide to see it and offer prayers.
Buland Darwaza
Buland Darwaza is in Fatehpur Sikri, which is 43 km from Agra. This is also the main entrance of Fatehpur Sikri palace. Considered to be the world’s tallest and largest gate, the Buland Darwaza was built by Mughal Emperor Akbar in 1576 to celebrate his victory over the Gujarat Empire.

In 1601 AD, the Mughal Emperor Akbar built the Buland Darwaza at Fatehpur Sikri to commemorate his victory over Gujarat. The Buland Darwaza is 53.63 meters high and 35 meters wide. It is made of red sandstone and marble in distinct Mughal architecture with carved verses from the Holy Quran. The inscription of the Holy Quran is a symbol of the religious broad-mindedness of Akbar.
The Persian inscription on the Buland Darwaza reflects Akbar’s open-mindedness and is often used by historians as an example of diverse traditions and culture.
This elaborate, solid sandstone structure appears like the wisdom door of a large tomb from all sides. Many visitors come here to experience the peaceful scenery and study the beautiful wall art. The Buland Darwaza is built of red sandstone with white and black marble carvings on the interiors.
Built in symmetrical plan and parapet style, the structure is surmounted by pillars and chhatris. This door made of red stones was once used to stand guard at the south-eastern entrance of Fatehpur Sikri.
The Jama Masjid is also covered under this huge door, which is situated on the right side of the Buland Darwaza. This place attracts a lot of tourists.
Agra Fort
Agra Fort is located in the city of Agra in Uttar Pradesh, India. It is a UNESCO declared World Heritage Site. This fort is located 2.5 km north-west of the famous Taj Mahal. The Agra Fort is said to be the sister monument of the Taj Mahal. The monument was built by Akbar and is home to some important buildings like the Moti Masjid. Here Meena Bazar and Jahangir Mahal, which was built for Jahangir and his family. That too is situated.
The fort is also described as a large majestic city with a wall. Agra Fort was built by Akbar in red sandstone. Built through the unification of his kingdom after his accession to power in 1654, Agra Fort served as both a military strategic point and a royal residence.
There is a plaque at the entrance of the fort, which states that the fort was originally constructed before 1000 AD and was only renovated by Akbar. Later Shah Jahan made it more advanced. He made it even more spectacular with marble and beautiful carvings.
The fort is built in the shape of a crescent and is situated in front of the Yamuna River. It has ramparts, between which there are equal intervals of heavy bastions. When Babur defeated and killed Ibrahim Lodi at Panipat in 1526, Agra was an important seat of the Mughal Empire. It was in a ruined condition and then Akbar decided to make it his capital and Akbar, who reached Agra in 1558, had it rebuilt with red sandstone.
In the last days of his life, Shah Jahan’s son Aurangzeb imprisoned him in this fort. It is also said that Shah Jahan died while looking at the Taj in the fort’s Musamman Burj, which offers a clear view of the Taj Mahal. Agra Fort is famous all over the country as well as abroad.
Qutub Minar
Qutub Minar is located in the country’s capital Delhi. Whose construction was started in 1192 by Qutb-ud-Din Aibak. After which his successor Iltutmish and Firoz Shah Tughlaq completed its construction. Qutub Minar is a World Heritage Site. Although Qutub Minar was not built by the Mughals, it is still a witness to the amazing architecture of that time.
Qutb-ud-din Aibak was the founder of the Delhi Sultanate at that time. To complete the Qutub Minar, the successor Aibak built three more minarets in it. The Qutb Minar is named after Qutb-ud-din Aibak, the Sultanate of Delhi, and its builder Bakhtiyar Kaki was a Sufi saint.
It is said that the architecture of Qutub Minar was made in India before the arrival of Turkey. But according to the alleged facts, it was built after being inspired by the Rajput towers. We also see some parts of the history of Qutub Minar in Persian-Arabic and Nagari languages.
Whatever historical information is available regarding Qutub Minar, it has been received from Firoz Shah Tughlaq (1351-89) and Sikandar Lodi (1489-1517). The Quwwat-ul-Islam mosque is also situated to the north of the Qutub Minar, which was built by Qutub-ud-din Aibak in 1192.
This is considered to be a very ancient mosque of the Indian subcontinent. But later sometime Iltumish (1210-35) and Ala-ud-din Khilji developed the mosque. This great tower is 72.5 meters high and the base measures 14.32 meters and the top structure is 2.75 meters.
The Iron Pillar in Qutub Minar attracts many tourists. It is believed that if one stands with his back to the pillar and takes it with his arm then his wishes come true. The monument is an excellent example of Indo-Islamic Mughal architecture and is a famous tourist destination in Delhi.
If you don’t take your private vehicle to these places then you can visit these Mughal Architectures by taking a Delhi taxi service .